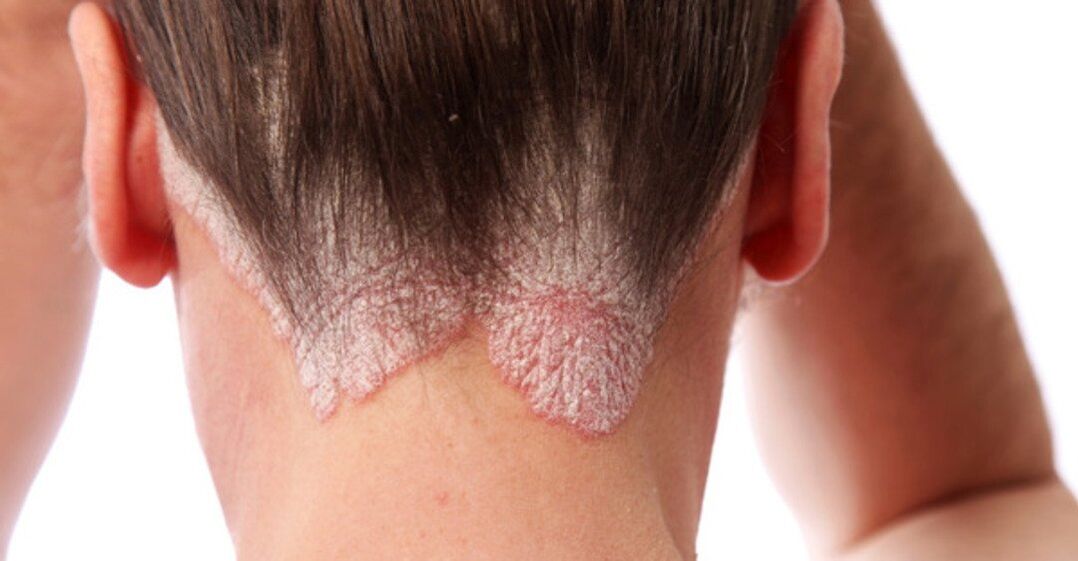
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease with an adverse combination of factors of genesis with a recurrent course, a variety of phenotypes, clinical varieties and the possible detection of various simultaneously undergoing chronic diseases.According to literature, the prevalence of psoriasis of the world is 4–7%.
According to K. Reich, the mild forms of the disease that affect less than 3-5% of the body area and do not give significant changes in the patient’s immune status, require only local treatment.Psoriasis of the moderate and severe course is a systemic, inflammatory process, leading to the development of concomitant pathologies or worsening them, and they themselves have a huge impact on the health and quality of life of the patient.
The problem of treating psoriasis does not lose its relevance and, despite the emergence of new modern methods of treatment, remains a difficult task requiring a personified approach.
For the treatment of psoriasis, there is a wide selection of local and systemic drugs, most of which model the immune system.When choosing personified therapy, the prevalence and severity of psoriasis, the stage of the process, its clinical form, as well as the attitude to the patient’s illness himself are taken into account.So, with the localization of rashes in the open areas of the skin - the face, the hairy part of the head and brush, the disease has a significant effect on the quality of life and causes severe psycho -emotional experiences.According to the study of G. Krueger et al.(2001), 40% of patients with psoriasis were disappointed with the ineffectiveness of the resulting treatment and 32% considered the treatment insufficient.
System therapy of psoriasis
Systemic glucocorticoids in a tablet form are extremely rare in connection with numerous side effects.However, as the drug “ambulance” to stabilize the psoriatic process with a progressive stage, erythroderma is advisable to use prolonged systemic glucocorticoids for intramuscular administration in the form of short courses.A similar approach to therapy avoids adverse side effects.
More than 40 years in the treatment of psoriasis, methotrexate is used.The mechanism of its action is associated with the inhibiting of dihydrofolateredustase, which turns Acidum Dihydrofolic into Tetrahydrofolic and is a donor of simple carbon groups in the synthesis of purine nucleotides and thymidylate necessary for DNA synthesis.In this regard, the simultaneous purpose of folic acid helps to avoid metabolic anemia.
Cyclosporin, a-cyclic polypeptide, isolated from the fungus TolyPocladium inflatum Gams, has an immunosuppressive effect by suppressing the activity of T cells and reducing their antigenic sensitivity due to the immune system.The drug has high effectiveness in the treatment of a common slowly flowing psoriasis, psoriatic erythroderma.
Since 1997, aromatic retinoids of the second generation have been used to treat refractory forms of psoriasis, the basis of the chemical formula of which is ACITIRETIN.The drug inhibits the proliferation of epidermis cells, normalizes the keratinization process, has an immunomodulating effect.The effectiveness of the product depends on the dose: higher doses lead to a faster resolution of psoriatic rashes.
Relatively recently, a new group of drugs appeared - biological drugs, which include recombinant protein substances, synthesized by biotechnological by living cells of animals, plants and microorganisms.Indications for the prescription of biological drugs are severe forms of psoriasis resistant to other system drugs.
Treatment of moderate and severe forms of psoriasis (more than 10% of the body surface) is carried out taking into account conditions in which the patient has several chronic diseases such as metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic fatty liver, and lipid metabolic disorders.According to statistical studies, such conditions for psoriasis are observed more often than in a general population.Thus, in the treatment of psoriasis, it is necessary to take into account the risk of side effects of the ongoing systemic therapy, respectively, the conditions in which the patient has several chronic diseases that are detected individually in each patient.Indeed, some pharmacological drugs can negatively affect cardiovascular and metabolic concomitant diseases.The connection between psoriasis and cardiac-metabolic disorders has important clinical consequences.Firstly, the systemic therapy of psoriasis can negatively affect metabolic concomitant diseases, especially in the case of continuous and prolonged treatment.In particular, methotrexate should be prescribed with caution in obesity, diabetes mellitus, not alcoholic fatty liver disease due to an increase in the risk of liver fibrosis.Cyclosporine, or can cause the appearance or aggravate the course of arterial hypertension, enhance insulin resistance and affect the metabolism of fatty acids, has a toxic effect.
Acitrotin also promotes hypertriglyceridemia and/or hypercholesterolemia.Thus, when conducting patients with psoriasis, it is necessary to take into account all the data.
A special place in the treatment of psoriasis is given phototherapy.The positive effect of ultraviolet radiation on the skin is associated with the selective inhibition of the T-cell of the immunity.According to the literature, the following areas of the action of phototherapy are distinguished: anti -inflammatory, artificial inhibition of immunity and anti -caulifier.The effect of ultraviolet rays on immunity is associated with a depth of penetration.UFB rays affect the epidermal keratinocytes and langergan cells, Ufa rays penetrate deeper layers of the skin and have an effect on dermal fibroblasts, dendritic cells and cells of the immune system.The positive effect of ultraviolet radiation is due to Apoptosis of T cells, a decrease in the number of Langerganes cells, a change in cytokines, growth factors (EGF, VEGF), adhesion and neuropeptides molecules.The purpose of phototherapy is advisable for a common skin process.
In the treatment of psoriasis, photochemotherapy (bullet-therapy) is used-the combined use of long-wave ultraviolet rays (Ufa) (320–400 Nm) and photosensitizer (8-methoxyPsoralen).Puva-therapy is one of the most effective methods for treating psoriasis, its prescription is advisable with a common vulgar and exudative psoriasis, the stubborn course of the disease, severe infiltration.Treatment is carried out according to the 3- or 4-rack irradiation methodology per week, on average, the course is 20-30 procedures.
Currently, selective phototherapy, a combination of wave radiation (280–320 Nm) have lost its position and is prescribed less and less for the treatment of psoriasis.The indication for its purpose is psoriasis, characterized by formations with a low content of inflamed cells.
Narrow-lane UFB therapy with the peak of emissions at a wavelength of 311 nm in high therapeutic efficiency is comparable to bullet-therapy, but unlike it does not require the use of a photosensitizer.It is carried out according to the 3-5-rack irradiation methodology per week with a course of 20-30 procedures.
For the treatment of limited vulgar psoriasis in a stationary stage, a highly effective therapeutic technique is an eximmary laser, which allows to deliver the monochromatic light of high intensity of the wavelength of 308 nm only to the affected area of the skin.
Local therapy
A fairly large selection of local products for the treatment of psoriasis includes, in particular, traditional ointments containing tar, naphthalan, ichthyol and salicylic acid.
When choosing topical therapy, an individual approach is important, on which the compliance of the patient with psoriasis will depend.So, due to the cosmetic impossibility of treatment, 40% of patients do not comply with the destination.
The effectiveness of topical corticosteroid drugs in the treatment of psoriasis is based on their pronounced effects on the modulation of immunity and a decrease in tissue inflammation.The action is associated with the mechanism of the complex of hormones and receptors, which penetrates the core of the target cell cell and increases the expression of genes encoding the synthesis of peptides inhibiting the activity of phospholipase.This mechanism leads to a decrease in the formation of inflammation mediators from phospholipids.Combined corticosteroid ointments and creams with salicylic acid are especially preferred.Local corticosteroid preparations are not shown for prolonged continuous treatment and suggest combination and rotational schemes, because prolonged use can lead to the development of side effects, such as skin atrophy, hypertrichosis, telangiectasia, steroid acne and oppression of the adrenal function.
Synthetic analogues of vitamin D3 have established themselves well as highly effective means against psoriasis.The most famous from this group are calcipotriol.The principle of action of the drug is based on the effect of softening of keratinized skin with vitamin D3: it inhibits the proliferation of keratinocytes and models skin differentiation, and also has an immunomodulating effect, in particular reducing the expression of IL-2 and information.Calcipotriol has a cumulative effect, and therefore the therapeutic effect is observed after 1-2 weeks.From the beginning of treatment.
Unlike topical steroids, long -term use of this group of drugs is possible.To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, the combined purpose of calcipotriol and topical steroids is possible.
The action of local Calcineurin inhibitors (Takrolimus and Pimecrolimus) is associated with the blocking of signal transduction of T-lymphocytes by inhibiting Calcineurin.It is most advisable to prescribe this group of drugs in case of localization of rashes on the face, because they do not have such side effects as topical steroids.
The value of the use of mitigating agents, in the treatment of psoriasis, is not in doubt: they soften the skin, reduce peeling and dryness, enhance its hydration, especially after ultraviolet exposure;contribute to a decrease in itching.The greatest effect is achieved when applying to wet skin after contact with water (bath, shower).The use of mitigating agents in the complex therapy of psoriasis reduces the total cost of treatment as a result of achieving stabilization of the disease and the onset of remission in shorter periods, which helps to reduce the stay of patients in the hospital.
Thus, the problem of treating psoriasis retains its relevance and remains a comprehensive task, aimed primarily at a personified approach to therapy, on which the compliance of the patient with psoriasis and prospective conducting patients will depend, taking into account coordinity.